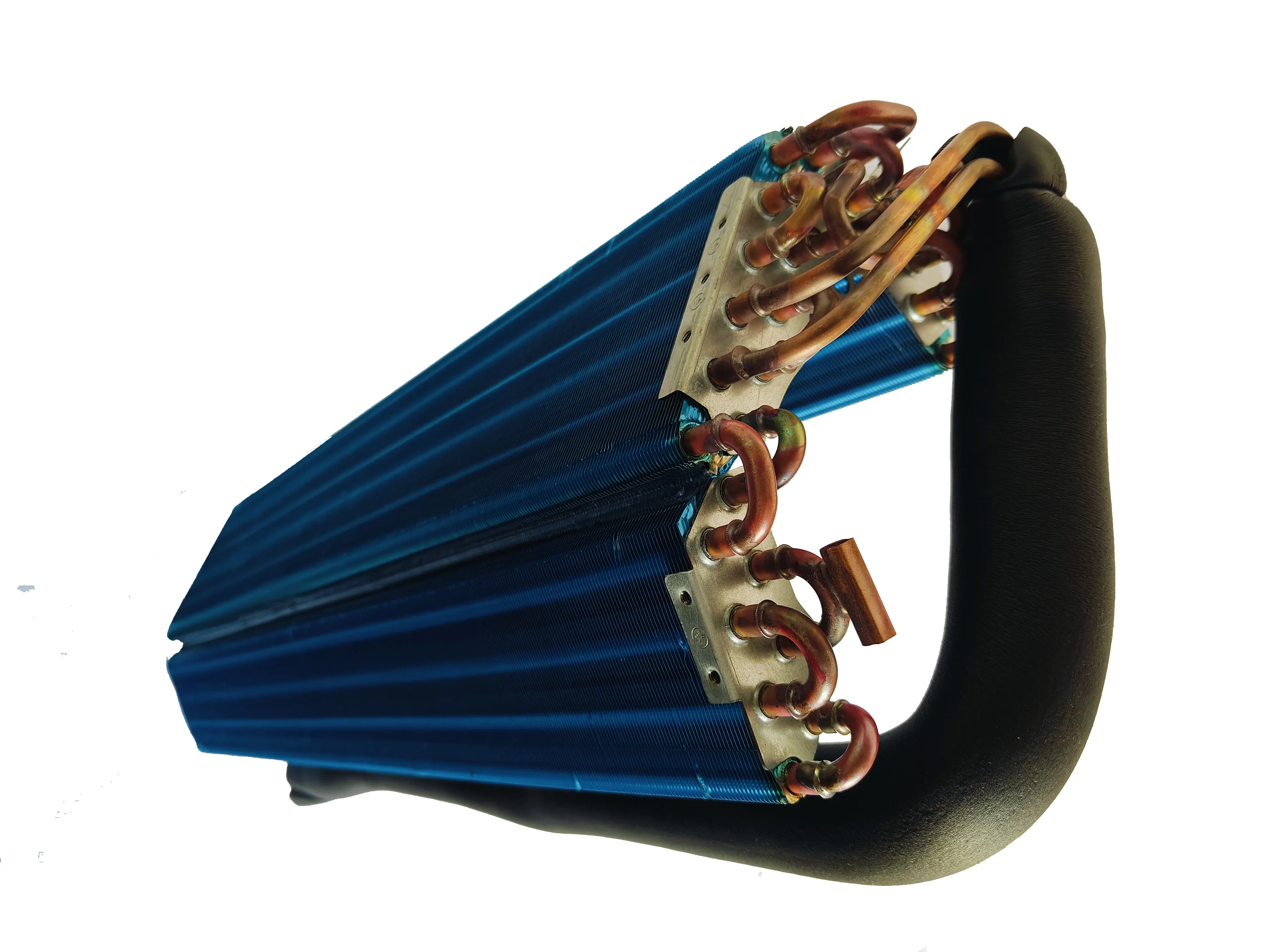
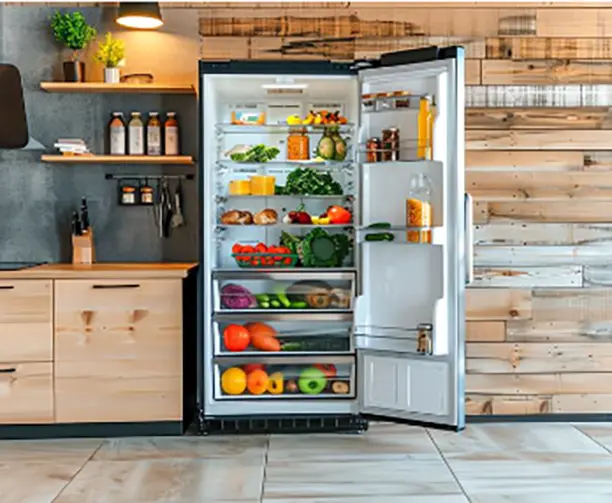
What is the impact of the fin spacing in a copper tube fin heat exchanger on its cooling performance?

The spacing between fins in a copper tube fin heat exchanger has several significant impacts on its cooling performance, as outlined below:
**Impact on Heat Transfer Efficiency**
- **Larger Fin Spacing:**
The air flows more smoothly through the exchanger with less resistance, reducing the likelihood of turbulence. However, the contact area between the air and the copper tubes is relatively smaller, limiting the volume of air participating in heat exchange. This reduces heat transfer efficiency, leading to a decrease in cooling capacity and coefficient of performance (COP).
- **Smaller Fin Spacing:**
The number of fins increases, enhancing the contact area between the air and the copper tubes and providing more opportunities for heat exchange. This improves the heat transfer coefficient, allowing heat to be more effectively transferred from the refrigerant inside the tubes to the air, thereby enhancing cooling performance. However, excessively small fin spacing can restrict airflow, increase turbulence, and ultimately reduce heat transfer efficiency.
**Impact on Airflow Resistance**
- **Larger Fin Spacing:**
The airflow passage is wider, resulting in lower resistance and reduced energy consumption for the fan, which lowers operating costs. However, the shorter contact time between the air and the fins may lead to insufficient heat exchange, negatively affecting cooling performance.
- **Smaller Fin Spacing:**
Airflow resistance increases significantly, requiring higher fan power to push air through the exchanger, which raises energy consumption. In severe cases, insufficient airflow can impair the overall performance of the heat exchanger, reducing cooling capacity.
**Impact on Frosting and Defrosting**
- **Larger Fin Spacing:**
After frost forms, the impact on airflow is relatively minor, as frost is less likely to block the channels. Additionally, frost in larger spaces is more susceptible to natural shedding or melting due to airflow and temperature changes, making defrosting easier and maintaining better cooling performance.
- **Smaller Fin Spacing:**
Frost accumulates more quickly and tends to build up between the fins, blocking airflow channels and reducing air volume. This deteriorates heat transfer and significantly lowers cooling performance. Moreover, smaller fin spacing makes defrosting more challenging, and incomplete defrosting can negatively affect the next cooling cycle.