Structure and working principle of refrigerator condenser
The refrigerator is one of the indispensable appliances in the modern household and its working principle is based on the refrigeration cycle. The condenser plays a crucial role in this process. The structure of a refrigerator condenser and its working principle will be described in detail below.
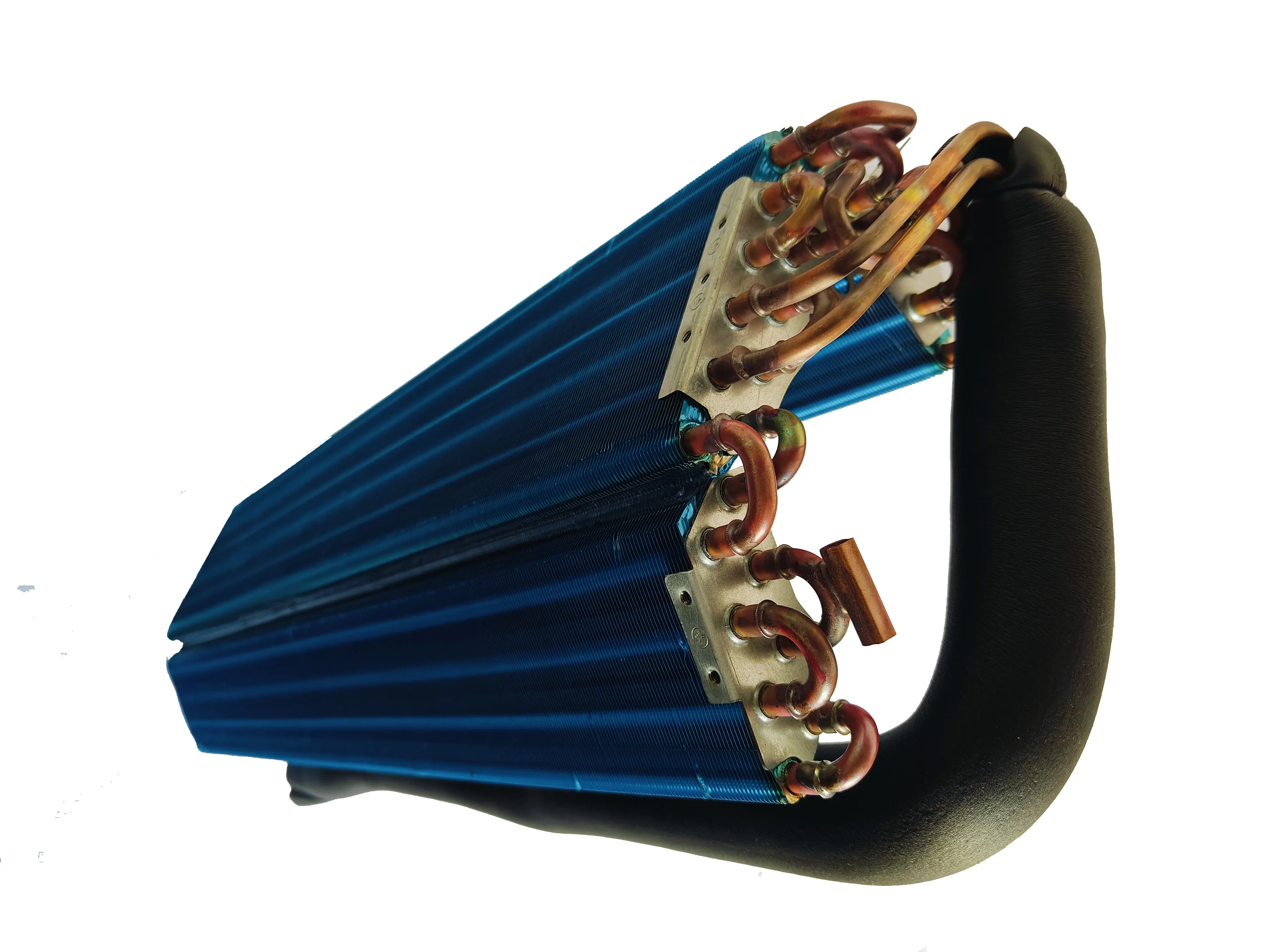
Structure of the condenser
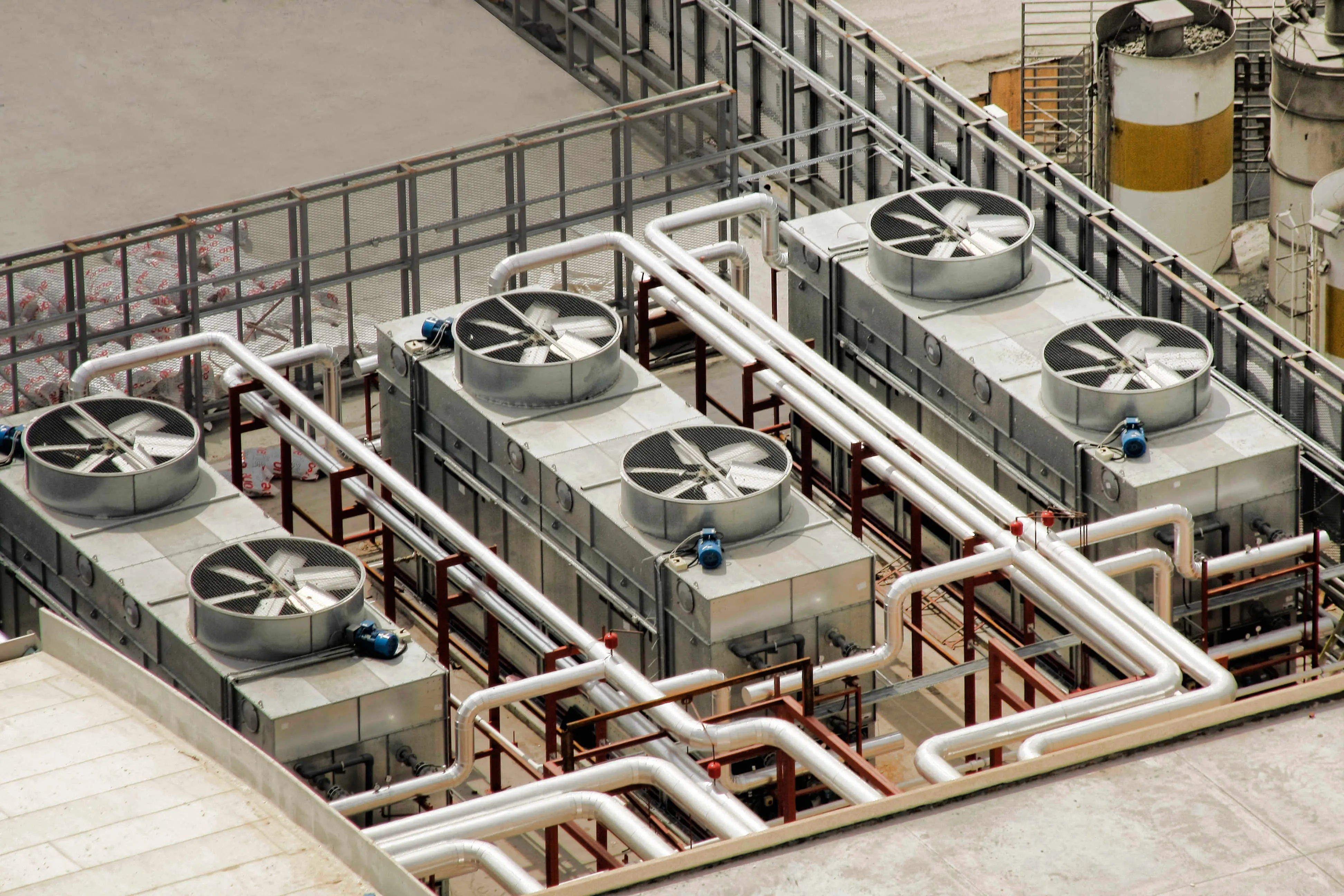
- Piping Design:A condenser usually consists of a series of thin copper or aluminum tubes that are designed to be serpentine or coiled to increase the contact area with the surrounding air.
- Heat sink:In order to increase heat exchange efficiency, heat sinks (also known as fins) are often installed on the outside of the condenser. These fins increase the surface area and help transfer heat to the surrounding air more efficiently.
- Fan :In some refrigerator designs, there will be one or more fans to help force air flow through the condenser, thus speeding up the heat exchange process.
- Connector:The condenser is connected to other refrigeration system components such as the compressor and evaporator through pipes to form a closed cycle system.
Working principle
- Compression process:The refrigerant is compressed into a high-temperature and high-pressure gas by the compressor.
- Condensation process:After the high-temperature and high-pressure gaseous refrigerant enters the condenser, it begins to release heat and gradually cools due to the temperature difference with the external environment (air). As the temperature drops, the refrigerant changes from gas to liquid. The heat released during this process is taken away by the air outside the condenser, which is why the condenser generates heat.
- Throttle expansion:The liquid refrigerant then passes through a throttling device (such as a capillary tube or expansion valve), where the pressure drops sharply, and the temperature also drops sharply, turning into a low-temperature and low-pressure liquid.
- Evaporation process:The low-temperature and low-pressure liquid refrigerant flows into the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from inside the refrigerator, increases its temperature, and is converted into a gas state again. At this time, the temperature inside the refrigerator drops and the cooling effect is achieved.
- Repeatedly:The above process is repeated continuously to form a complete refrigeration cycle.
In short, the condenser is one of the key components in the refrigerator refrigeration system. It is responsible for converting high-temperature and high-pressure gaseous refrigerant into a liquid state and discharging excess heat to the external environment. In this way, the condenser works in conjunction with other components to ensure that the refrigerator is able to maintain low temperatures continuously and effectively.