Southeast Asia’s Refrigeration Market: Heat Exchanger Selection for Humid Climates
Refrigeration systems in Southeast Asia face unique challenges due to the region’s hot and humid climate. High humidity diminishes cooling efficiency and forces users to lower thermostats excessively, leading to energy overuse. Elevated temperatures further strain refrigeration units, increasing operational costs. Corrosion risks, exacerbated by moisture exposure, demand durable solutions. Selecting the right heat exchanger, such as a Copper Fin Heat Exchanger, ensures reliable performance, reduced maintenance, and long-term savings.
Key Takeaways
- Southeast Asia's humid air makes refrigerators work less efficiently. Use heat exchangers made for wet places, like copper fin ones, to work better.
- Picking energy-saving heat exchangers can cut costs a lot. Look at plate and frame heat exchangers for better heat transfer.
- Rust is a big problem in humid areas. Use copper or aluminum heat exchangers to last longer and need less fixing.
Environmental Challenges in Southeast Asia

High Humidity and Refrigeration Efficiency
Humidity levels in Southeast Asia often exceed 80%, creating significant challenges for refrigeration systems. I’ve observed how high humidity reduces cooling efficiency by increasing the moisture content in the air. This forces refrigeration units to work harder to remove excess moisture, leading to higher energy consumption. The interaction between humidity and pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide, further complicates the situation. These pollutants accelerate the corrosion process, especially in areas with frequent precipitation.
Tip: To combat humidity-related inefficiencies, refrigeration systems should incorporate heat exchangers designed for moisture-heavy environments, such as copper fin heat exchangers.
Elevated Temperatures and Energy Consumption
Temperatures in Southeast Asia often exceed 30°C, significantly impacting energy consumption. Urban heat islands in cities like Bangkok and Bandung amplify this effect, increasing annual cooling degree days. I’ve seen studies showing that countries like Thailand and Vietnam experience rising energy demand for cooling due to prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures. This trend highlights the need for energy-efficient refrigeration systems that can withstand high thermal loads without compromising performance.
- Key Observations:
- Higher temperatures increase the workload on refrigeration systems.
- Urban heat islands exacerbate cooling energy demand.
- Cooling degree days correlate directly with energy consumption.
Corrosion Risks in Humid Climates
Corrosion remains one of the most pressing challenges for refrigeration systems in Southeast Asia. I’ve noticed how environmental factors like temperature, humidity, and pollutants interact to accelerate material degradation. The table below summarizes these factors:
| Environmental Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Influences the rate of corrosion and interacts with other factors like humidity. |
| Relative Humidity | A key factor in corrosion processes, affecting the moisture level on surfaces. |
| Pollutants | Includes nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide, which interact with humidity and temperature. |
| Solar Radiation | Affects temperature and can influence corrosion rates. |
| Precipitation | Contributes to moisture levels and can lead to increased corrosion. |
| Wind | Can affect the distribution of pollutants and moisture in the environment. |
Selecting corrosion-resistant materials, such as copper and aluminum, ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs. I recommend solutions like copper aluminum fin heat exchangers, which are specifically designed to withstand these harsh conditions.
Types of Heat Exchangers for Humid Climates

Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Air-cooled heat exchangers are widely used in humid climates due to their simplicity and reliability. I’ve observed how these systems leverage ambient air to dissipate heat, making them ideal for regions with limited water resources. Counter flow arrangements enhance their performance, as studies show they improve heat transfer efficiency significantly.
- Key Advantages:
- Minimal water usage, reducing operational costs.
- Effective in environments with high humidity when paired with finned tube designs.
Recent experiments on spiral-coil finned tube heat exchangers validate their effectiveness under dehumidifying conditions. The results showed an average error of only 1.2% for enthalpy and 4.0% for humidity effectiveness, proving their reliability in challenging climates.
Water-Cooled Heat Exchangers
Water-cooled heat exchangers excel in humid climates where water is abundant. I’ve seen how these systems utilize water as a cooling medium, offering superior heat transfer capabilities compared to air-cooled alternatives. Their three heat transfer processes—convective, conductive, and convective—make them particularly effective in hot and humid conditions.
| Heat Exchanger Type | Configuration | Performance Metrics | Climate Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Air Heat Exchanger (WAHE) | Three heat transfer processes | Enhanced heat transfer efficiency | Hot humid climate (Am) |
These systems are ideal for applications requiring high cooling loads, such as industrial refrigeration. However, they demand proper maintenance to prevent scaling and corrosion, which can compromise performance over time.
Plate Heat Exchangers
Plate heat exchangers are compact and highly efficient, making them a popular choice for humid climates. I’ve noticed how their design allows for maximum heat transfer while minimizing space requirements. Empirical data highlights their performance under varying humidity levels:
| Relative Humidity Range | Description of Processes |
|---|---|
| RH < 30% | No mass transfer occurs. |
| RH = 30% to 80% | Balanced condensation and vaporization processes. |
| RH > 80% | Moisture accumulation observed, leading to frost formation. |
These systems outperform shell-and-tube and concentric heat exchangers, especially in environments with high humidity. Their ability to handle moisture-heavy conditions without significant efficiency loss makes them a reliable option for Southeast Asia’s climate.
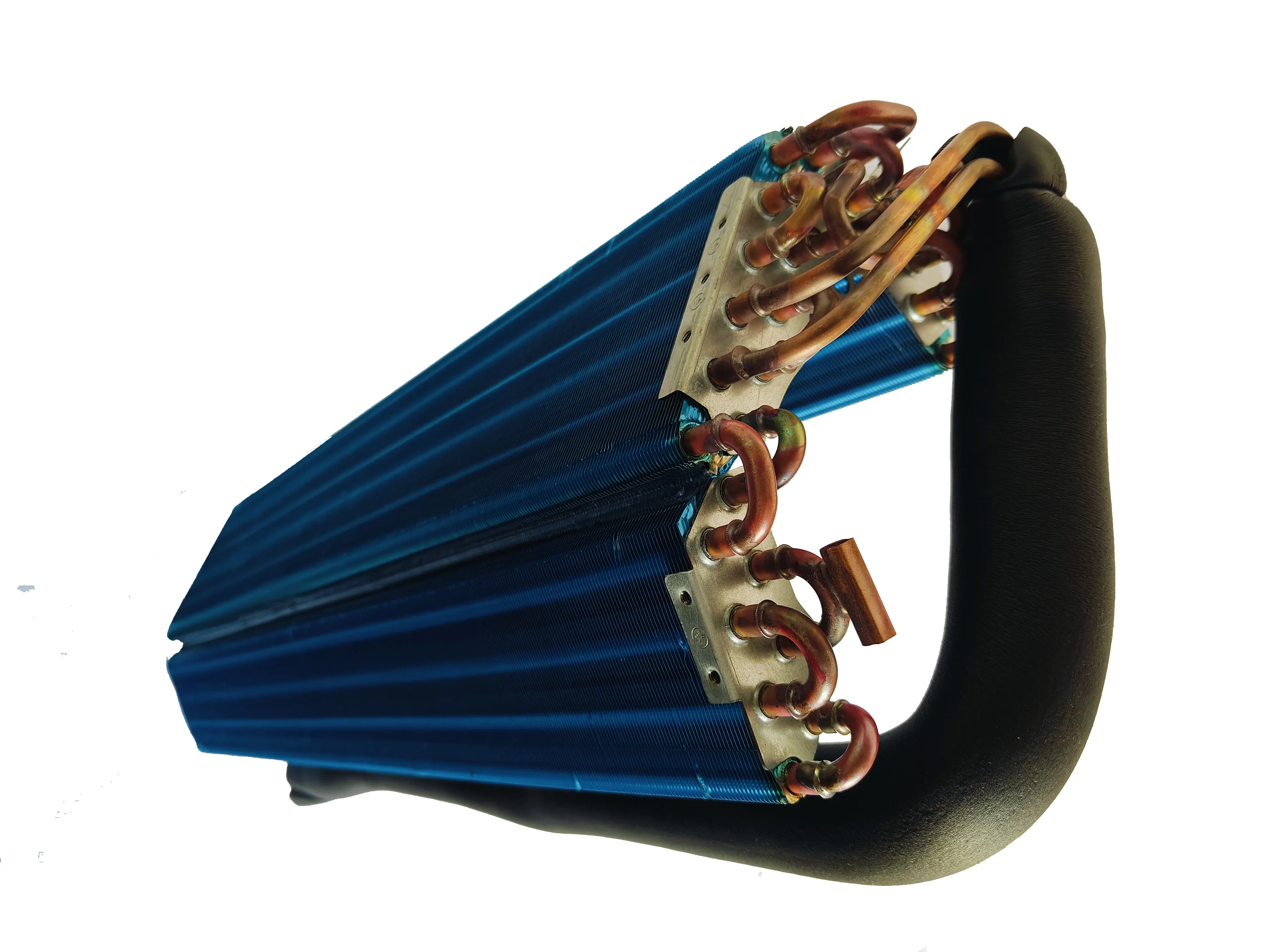
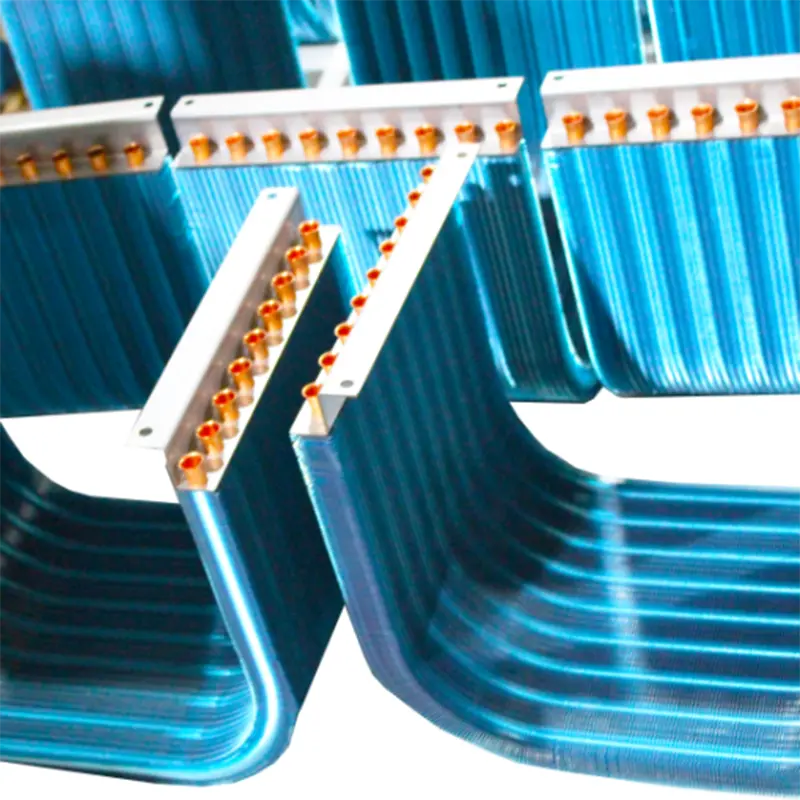
Copper Fin Heat Exchanger
Copper fin heat exchangers stand out for their exceptional thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. I’ve seen firsthand how copper’s thermal conductivity of 231 Btu/(hr-ft-F) enhances heat transfer efficiency, outperforming aluminum by 60% and stainless steel by nearly 30 times.
- Key Benefits:
- Superior corrosion resistance, crucial for humid environments.
- High thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat exchange.
Copper fin heat exchangers are particularly effective in mitigating corrosion caused by pollutants and moisture. Their durability makes them ideal for applications like refrigerators, freezers, and dehumidifiers. Companies like senjun specialize in producing these heat exchangers, ensuring reliable performance in Southeast Asia’s challenging climate.
Criteria for Selecting Heat Exchangers
Material Durability and Corrosion Resistance
In Southeast Asia’s humid climate, material durability plays a critical role in the performance of heat exchangers. I’ve observed how high humidity, combined with pollutants like sulfur dioxide, accelerates corrosion. This makes corrosion-resistant materials, such as copper and aluminum, essential for long-lasting systems. Copper, in particular, stands out due to its superior resistance to moisture-induced degradation. For example, copper fin heat exchangers not only resist corrosion but also maintain their thermal efficiency over time, making them a reliable choice for humid environments.
Tip: Always prioritize heat exchangers made from materials that can withstand both high humidity and pollutant exposure. This reduces maintenance needs and extends the equipment’s lifespan.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
Energy efficiency directly impacts operational costs, especially in regions with high cooling demands like Southeast Asia. I’ve seen how selecting the right heat exchanger can significantly reduce energy consumption. For instance, plate and frame heat exchangers offer high heat transfer efficiency while maintaining a compact design. The table below highlights key features and maintenance considerations for various heat exchanger types:
| Heat Exchanger Type | Key Features | Maintenance Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Shell and Tube | Effective for large capacities | Regular cleaning to prevent fouling |
| Plate and Frame | High heat transfer efficiency | Periodic inspections for leaks |
| Air-Cooled | Utilizes ambient air, often finned | Vibration monitoring for performance |
| Double Pipe | Simple design, suitable for small loads | Performance monitoring to track efficiency |
By choosing energy-efficient designs, businesses can lower their operational costs while meeting the cooling demands of humid climates.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance ensures the longevity and reliability of heat exchangers. I’ve noticed that predictive maintenance strategies can extend equipment life by up to 30% while reducing costs by 20-25%. Maintaining detailed records of maintenance activities is equally important. These records help track performance, identify recurring issues, and optimize preventive maintenance schedules. Here are some key maintenance strategies and their benefits:
- Predictive maintenance reduces unexpected downtime and extends equipment life.
- Lifecycle management improves customer satisfaction and lowers running costs.
- Custom maintenance plans minimize downtime and align with specific budget needs.
Note: Historical maintenance data is invaluable. It helps analyze the effectiveness of existing checks and ensures safe, reliable operation.
Compatibility with Refrigeration Systems
Compatibility with existing refrigeration systems is a crucial factor when selecting heat exchangers. I’ve seen how adiabatic pre-cooling systems, when paired with air-cooled condensers, enhance cooling performance in humid climates. These systems improve energy efficiency by reducing the workload on refrigeration units. Additionally, the configuration of heat exchangers must align with the specific requirements of the refrigeration system to ensure optimal performance.
- Studies show that adiabatic pre-cooling systems are particularly effective in regions with high atmospheric moisture.
- Properly configured systems enhance energy efficiency and cooling performance.
Selecting the right heat exchanger ensures seamless integration with refrigeration systems, reducing energy consumption and improving overall efficiency.
Real-World Applications and Innovations
Case Studies from Southeast Asia
I’ve seen how businesses in Southeast Asia adapt refrigeration systems to overcome the region’s humid climate. For example, a food processing company in Thailand implemented copper fin heat exchangers to enhance cooling efficiency in their storage facilities. The results were remarkable. Their energy consumption dropped by 15%, and maintenance costs decreased due to the corrosion-resistant properties of copper. In Vietnam, a beverage manufacturer faced challenges with high humidity affecting product quality. They upgraded their refrigeration systems with plate heat exchangers, which improved temperature control and reduced operational downtime. These examples highlight the importance of selecting the right heat exchanger for specific applications.
Lessons from Other Tropical Regions
Other tropical regions offer valuable insights into managing refrigeration challenges. In Brazil, I’ve observed how industries use water-cooled heat exchangers to handle high cooling loads in humid conditions. Their approach focuses on optimizing water usage while maintaining efficiency. Similarly, in India, businesses leverage adiabatic cooling systems to reduce energy consumption during peak summer months. These strategies demonstrate the importance of tailoring heat exchanger solutions to local environmental factors. Southeast Asia can benefit from adopting similar practices, especially in industries with high cooling demands.
Innovations by Companies like senjun
Companies like senjun lead the way in developing advanced heat exchanger technologies. I’ve explored their copper aluminum fin heat exchangers, which are designed to withstand Southeast Asia’s humid climate. Their products, including wire tube condensers, offer exceptional durability and efficiency. Senjun’s innovations cater to diverse applications, from medical ultra-low temperature refrigerators to dehumidifiers. Their focus on research and development ensures that businesses in the region have access to reliable and cost-effective solutions. By integrating senjun’s heat exchangers, industries can achieve long-term savings and improved performance.
Selecting the right heat exchanger for Southeast Asia’s humid climate requires careful evaluation. I prioritize durability, energy efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Copper Fin Heat Exchangers excel in these areas, offering reliable performance and corrosion resistance. Stakeholders should explore innovative solutions from companies like senjun to ensure long-term savings and operational success.
FAQ
What makes copper fin heat exchangers ideal for humid climates?
Copper fin heat exchangers resist corrosion and offer superior thermal conductivity. Their durability ensures reliable performance in moisture-heavy environments like Southeast Asia.
How can businesses reduce maintenance costs for heat exchangers?
Predictive maintenance strategies help identify issues early. Regular inspections and lifecycle management extend equipment life and minimize unexpected downtime.
Why should I consider senjun heat exchangers for my refrigeration needs?
Senjun specializes in durable, efficient heat exchangers. Their copper aluminum fin designs cater to diverse applications, ensuring long-term savings and optimal performance.