Key EU CE Certification Requirements for Exporting Refrigeration Parts

I believe CE certification plays a vital role in accessing the EU market for refrigeration parts. It ensures that products meet strict safety, health, and environmental standards. For exporters like Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd., this certification is not just a requirement but a gateway to success. Their expertise in producing components such as the wire tube condenser highlights their commitment to quality and compliance. Following the certification process carefully helps avoid penalties and ensures smooth market entry.
Key Takeaways
- CE certification is needed to sell in the EU. It shows products are safe and follow health and environmental rules.
- Find the right CE rules for your product type. This makes the process easier and avoids fines.
- Keep clear technical records. Include product details, test results, and rule updates to stay compliant.
- Use a Notified Body for risky products. They check safety and rules, helping you enter the market easily.
- Learn about rule changes often. Update your work and records to stay compliant and gain customer trust.
Identifying Applicable CE Directives for Refrigeration Parts

Overview of Relevant Directives
Pressure Equipment Directive (PED)
I always start by considering the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) when dealing with refrigeration parts. This directive applies to equipment operating under pressure, such as systems using refrigerants. Recent updates emphasize the transition to low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants. These changes align with EU regulations to reduce F-gas emissions. However, this shift often reclassifies products as "dangerous," requiring stricter compliance measures. For some products, a Notified Body must conduct a conformity assessment to ensure safety.
Machinery Directive
The Machinery Directive focuses on the mechanical safety of equipment. For refrigeration parts, this includes ensuring that moving components, such as fans or compressors, operate safely. I find this directive particularly relevant for products integrated into larger systems like refrigerators or freezers.
Low Voltage Directive (LVD)
The Low Voltage Directive (LVD) ensures electrical safety for products operating within specific voltage ranges. For refrigeration parts like wire tube condensers, this directive applies if the product includes electrical components. Manufacturers must demonstrate that their products meet these safety standards to prevent electrical hazards.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive
The EMC Directive addresses electromagnetic interference. I always check this directive for products with electronic controls or components. It ensures that refrigeration parts do not interfere with other electronic devices and function correctly in their intended environment.
Determining Which Directives Apply to Your Product
Factors such as product type, function, and intended use
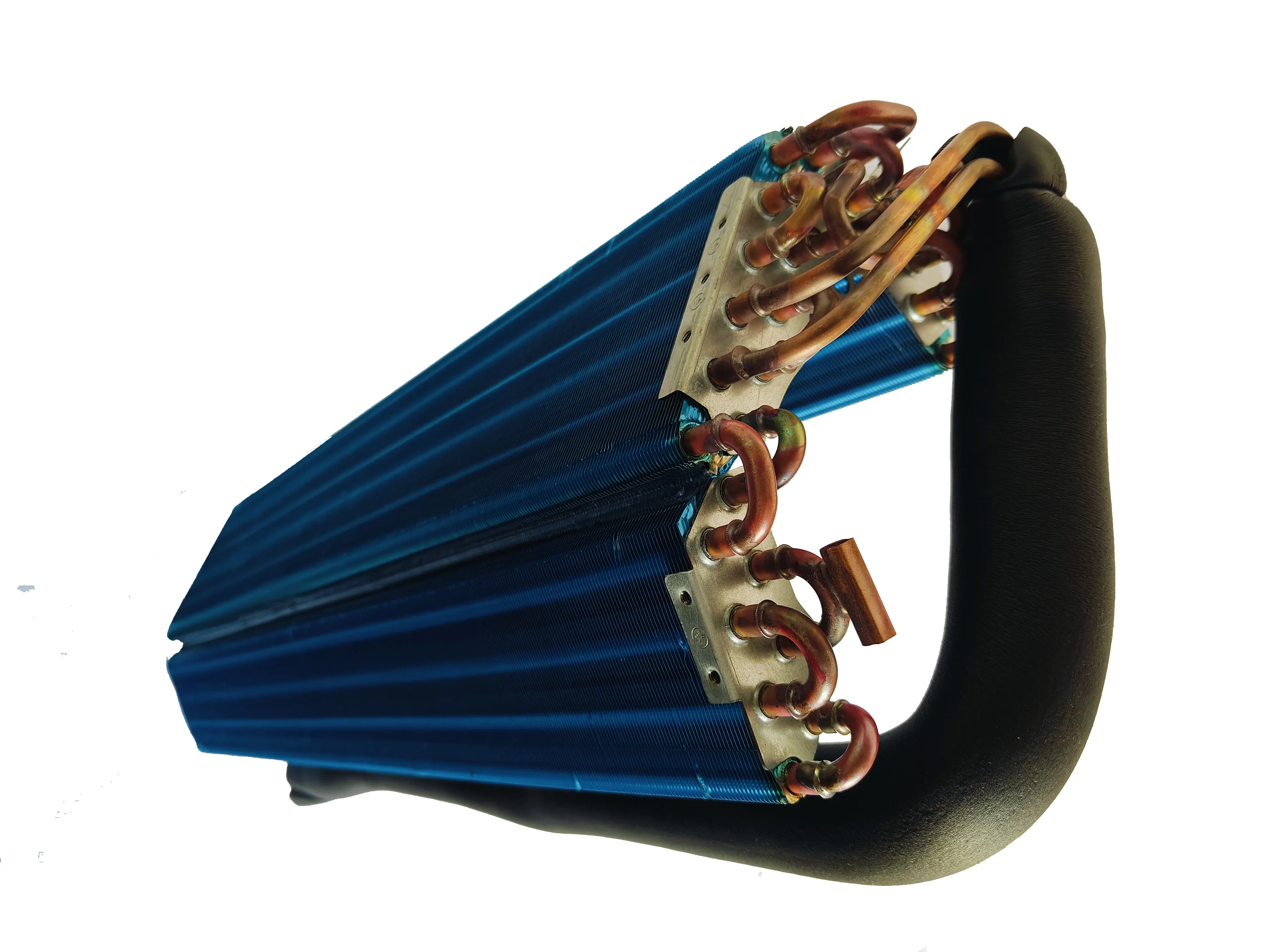
To determine which directives apply, I evaluate the product's type, function, and intended use. For example, a wire tube condenser used in a refrigerator must comply with the PED and LVD if it operates under pressure and includes electrical components. Understanding these factors helps me identify the relevant directives and avoid unnecessary assessments.
Examples of refrigeration parts, including wire tube condensers, and their applicable directives
Let’s take wire tube condensers as an example. These components often fall under the PED due to their role in heat exchange systems. If they include electrical elements, the LVD also applies. For products with electronic controls, the EMC Directive becomes relevant. By analyzing the product's features and intended application, I can pinpoint the necessary directives and streamline the certification process.
Essential Requirements for Refrigeration Parts
General Safety and Performance Standards
Mechanical safety
I always emphasize the importance of mechanical safety when working with refrigeration parts. Products must be designed to prevent mechanical hazards, such as sharp edges or moving parts that could cause injury. For example, fans and compressors in refrigeration systems should include protective covers to ensure user safety. Standards like ASHRAE Standard 15-2024 provide updated guidelines for pressure relief devices, ensuring safe operation under varying conditions. These updates also improve the dispersal of refrigerants, reducing risks during maintenance or emergencies.
Electrical safety
Electrical safety is equally critical. Refrigeration parts must comply with standards that prevent electrical shocks, short circuits, or overheating. For instance, wire tube condensers with electrical components must meet the Low Voltage Directive requirements. ASHRAE Standard 34-2024 enhances safety classifications by updating toxicity values for refrigerants, ensuring safer designs. These measures not only protect users but also improve product reliability.
Environmental and Energy Efficiency Requirements
Compliance with F-Gas Regulation
The F-Gas Regulation aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by phasing out high-GWP refrigerants. I always recommend using low-GWP alternatives to meet these requirements. For refrigeration parts, this means selecting refrigerants that align with EU environmental goals. Compliance ensures market access and contributes to global sustainability efforts.
Energy-related Product (ErP) Directive
Energy efficiency is another key requirement. The ErP Directive mandates that products meet minimum energy performance standards. For refrigeration parts like wire tube condensers, this involves optimizing heat exchange efficiency. Meeting these standards not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers operating costs for end-users.
Specific Requirements for Hazardous Substances
Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
The RoHS Directive restricts the use of hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium in electrical and electronic equipment. I always ensure that refrigeration parts comply with this directive to minimize environmental impact. For example, using RoHS-compliant materials in wire tube condensers helps manufacturers meet EU standards while promoting eco-friendly practices.
Third-Party Certification: When Is It Required?
Self-Certification vs. Notified Body Involvement
When self-certification is sufficient
I often find that self-certification works well for low-risk refrigeration parts. Manufacturers can assess their products against the applicable CE directives and harmonized standards without external involvement. For example, wire tube condensers that do not include electrical or pressurized components typically qualify for self-certification. This approach saves time and resources while still ensuring compliance with EU regulations. However, I always recommend thorough internal testing to avoid any compliance issues later.
When third-party assessment is mandatory
For high-risk products, third-party assessment becomes essential. Directives like the Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) or the Gas Appliances Regulation (GAR) often require a Notified Body to verify conformity. These assessments ensure that products meet stringent safety and performance standards. For instance, refrigeration parts operating under high pressure or using hazardous refrigerants must undergo this process. I see this as a critical step for ensuring both product safety and market access.
Role of Notified Bodies in the Certification Process
Testing and verification of compliance
Notified Bodies play a vital role in testing and verifying compliance. They evaluate products against technical requirements and harmonized standards. This process reduces the risk of noncompliance, which remains a significant issue. In 2022, 62.12% of products showed some form of noncompliance. I believe involving a Notified Body minimizes such risks and ensures a smoother certification process.
Issuance of certificates for high-risk products
For high-risk refrigeration parts, Notified Bodies issue certificates of conformity. These certificates, such as the PED Certificate of Conformity, are often mandatory for CE marking. They enable manufacturers to confidently enter the EU market. According to Apex Cool, this certification demonstrates compliance with health, safety, and environmental standards. I see this as not just a regulatory requirement but also a mark of quality and reliability.
| Evidence Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Apex Cool | The CE certificate indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection requirements, essential for market access in the EU. |
| Gas Appliances Regulation | The GAR mandates third-party involvement in product conformity assessments, ensuring safety and compliance. |
| Pressure Equipment Directive | A PED Certificate of Conformity is often required for CE marking, facilitating market entry in the EEA. |
By understanding when to involve a Notified Body, I can ensure that refrigeration parts meet all necessary requirements, paving the way for successful EU market entry.
Assessing Product Conformity
Steps in the Conformity Assessment Process
Risk assessment and hazard analysis
I always begin the conformity assessment process with a thorough risk assessment and hazard analysis. This step identifies potential risks associated with refrigeration parts, such as mechanical failures or electrical hazards. For example, when evaluating a wire tube condenser, I examine its design and materials to ensure it can withstand operational pressures and temperatures. This analysis helps me address safety concerns early, reducing the likelihood of accidents or product recalls.
Testing against harmonized standards
After completing the risk assessment, I test the product against harmonized standards. These standards provide clear benchmarks for safety, performance, and environmental compliance. For refrigeration parts, this includes testing for pressure resistance, energy efficiency, and material safety. By adhering to these standards, I ensure that the product meets EU requirements and performs reliably in real-world applications.
| Certification/Regulation | Description |
|---|---|
| Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) | A mandatory EU regulation for pressure equipment design, manufacture, and conformity assessment, crucial for market access in the EEA. |
Using Harmonized Standards for Compliance
Benefits of harmonized standards
Harmonized standards offer several benefits. They ensure safety by identifying potential hazards and setting clear safety benchmarks. These standards also improve product quality by addressing design flaws before market release. I find that compliance with harmonized standards enhances brand reputation and customer trust. It also reduces legal risks by demonstrating due diligence in meeting regulatory requirements.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Ensuring safety | Identifies potential hazards and ensures appliances meet safety standards to prevent accidents. |
| Compliance | Mandatory for commercial refrigerating appliances in the U.S., ensuring adherence to regulations. |
| Improved quality | Identifies design flaws that can affect performance, enhancing product longevity before market release. |
| Competitive advantage | Enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty through compliance with safety standards. |
| Liability protection | Demonstrates due diligence, reducing legal risks for manufacturers and retailers. |
Examples of standards for refrigeration parts, including wire tube condensers
For refrigeration parts like wire tube condensers, harmonized standards cover various aspects. These include EN 378 for refrigeration systems and ISO 5149 for safety and environmental requirements. These standards ensure that products operate safely and efficiently while minimizing environmental impact. By following these guidelines, I can confidently certify refrigeration parts for the EU market.
Creating and Maintaining Technical Documentation
Components of Technical Documentation
Product description and intended use
I always start technical documentation with a clear product description and its intended use. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the refrigeration part, such as a wire tube condenser, including its purpose and how it fits into larger systems like refrigerators or freezers. A well-written description ensures that anyone reviewing the documentation understands the product's role and functionality.
Design and manufacturing details
Next, I include detailed information about the product's design and manufacturing process. This section covers materials used, dimensions, and assembly methods. For example, when documenting a wire tube condenser, I specify the type of tubing, coating materials, and welding techniques. These details demonstrate compliance with EU standards and help identify potential risks during the conformity assessment process.
Test reports and risk assessments
Test reports and risk assessments form the backbone of technical documentation. They validate the product's compliance with applicable CE directives and harmonized standards. For refrigeration parts, these reports might include pressure resistance tests or energy efficiency evaluations. I ensure that all test results are accurate and well-documented to avoid delays in the certification process.
| Required Element | Description |
|---|---|
| General Description | A comprehensive overview of the appliance is necessary for compliance. |
| Test Reports | Essential for assessing conformity with relevant directives. |
Importance of Keeping Documentation Updated
Changes in product design or regulations
I always update technical documentation when there are changes in product design or EU regulations. For instance, if a new directive introduces stricter requirements for refrigerants, I revise the documentation to reflect these updates. Staying proactive ensures continued compliance and avoids potential penalties.
Retention period for technical files
Maintaining documentation for the required retention period is equally important. EU regulations typically mandate that manufacturers keep technical files for at least ten years after the product's last production date. I treat this as a critical responsibility to ensure traceability and accountability throughout the product's lifecycle.
Keeping technical documentation accurate and up-to-date not only ensures compliance but also builds trust with customers and regulatory bodies. It’s a cornerstone of successful market access in the EU.
Declaration of Conformity and Affixing the CE Mark

Drafting the Declaration of Conformity
Required information in the declaration
When drafting the Declaration of Conformity, I always ensure it includes all essential details. This document certifies that the product complies with applicable CE directives and standards. It must clearly identify the product, including its model and serial number. I also include the manufacturer's name, address, and contact information. Listing the relevant CE directives and harmonized standards is crucial. For refrigeration parts, this might involve directives like the Pressure Equipment Directive or the Low Voltage Directive. Additionally, I specify where the technical documentation, such as test reports, is stored. This ensures that the document is both comprehensive and easy to verify.
Template and examples
To simplify the process, I follow a structured template. For example:
- Product Identification: Wire Tube Condenser, Model XYZ123
- Manufacturer Details: Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd., Address, Contact Info
- Applicable Directives: PED, LVD, RoHS
- Standards Applied: EN 378, ISO 5149
This format ensures clarity and compliance. I always double-check the document for accuracy before issuing it.
Properly Affixing the CE Mark
Placement and visibility requirements
The CE mark must be visible, legible, and permanent. I usually place it directly on the product. If that’s not possible, I affix it to the packaging or accompanying documents. For refrigeration parts like wire tube condensers, the mark should be easy to locate and read. It must follow the proportional dimensions specified by EU guidelines. This ensures that the mark meets regulatory requirements and avoids any confusion.
Common mistakes to avoid
I’ve seen manufacturers make errors like using incorrect proportions for the CE mark or placing it in hard-to-see locations. Another common mistake is affixing the mark before completing the conformity assessment. To avoid these issues, I always ensure the product fully complies with all directives before adding the CE mark. This approach not only ensures compliance but also builds trust with customers and regulators.
Properly drafting the Declaration of Conformity and affixing the CE mark are critical steps. They demonstrate a commitment to safety, quality, and regulatory compliance, paving the way for successful market entry in the EU.
Achieving CE certification for refrigeration parts involves several critical steps. I always recommend identifying applicable directives, ensuring compliance with harmonized standards, and maintaining accurate technical documentation. For exporters like Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd., this process ensures that products, such as the wire tube condenser, meet EU safety and environmental standards. Staying compliant not only facilitates market access but also builds trust with customers. I encourage manufacturers to monitor regulatory updates and consult experts when needed to navigate this complex process effectively.
FAQ
What is the purpose of CE certification?
CE certification ensures that products meet EU safety, health, and environmental standards. It allows manufacturers to sell their products in the European Economic Area (EEA). I see it as a way to demonstrate compliance and build trust with customers.
Do all refrigeration parts require CE marking?
Not all refrigeration parts need CE marking. It depends on the product type and applicable directives. For example, wire tube condensers without electrical components may not require CE marking. I always recommend checking the relevant EU directives.
How long does the CE certification process take?
The timeline varies based on the product's complexity and the directives involved. Simple products may take a few weeks, while high-risk items requiring third-party assessments could take months. I suggest starting early to avoid delays.
Can I self-certify my refrigeration parts?
Yes, self-certification is possible for low-risk products. Manufacturers must ensure compliance with applicable directives and maintain proper documentation. For high-risk items, I recommend involving a Notified Body for certification.
What happens if my product fails to meet CE requirements?
Noncompliance can lead to penalties, product recalls, or market access restrictions. I always advise conducting thorough testing and documentation to avoid these issues. Staying proactive ensures smooth certification and market entry.