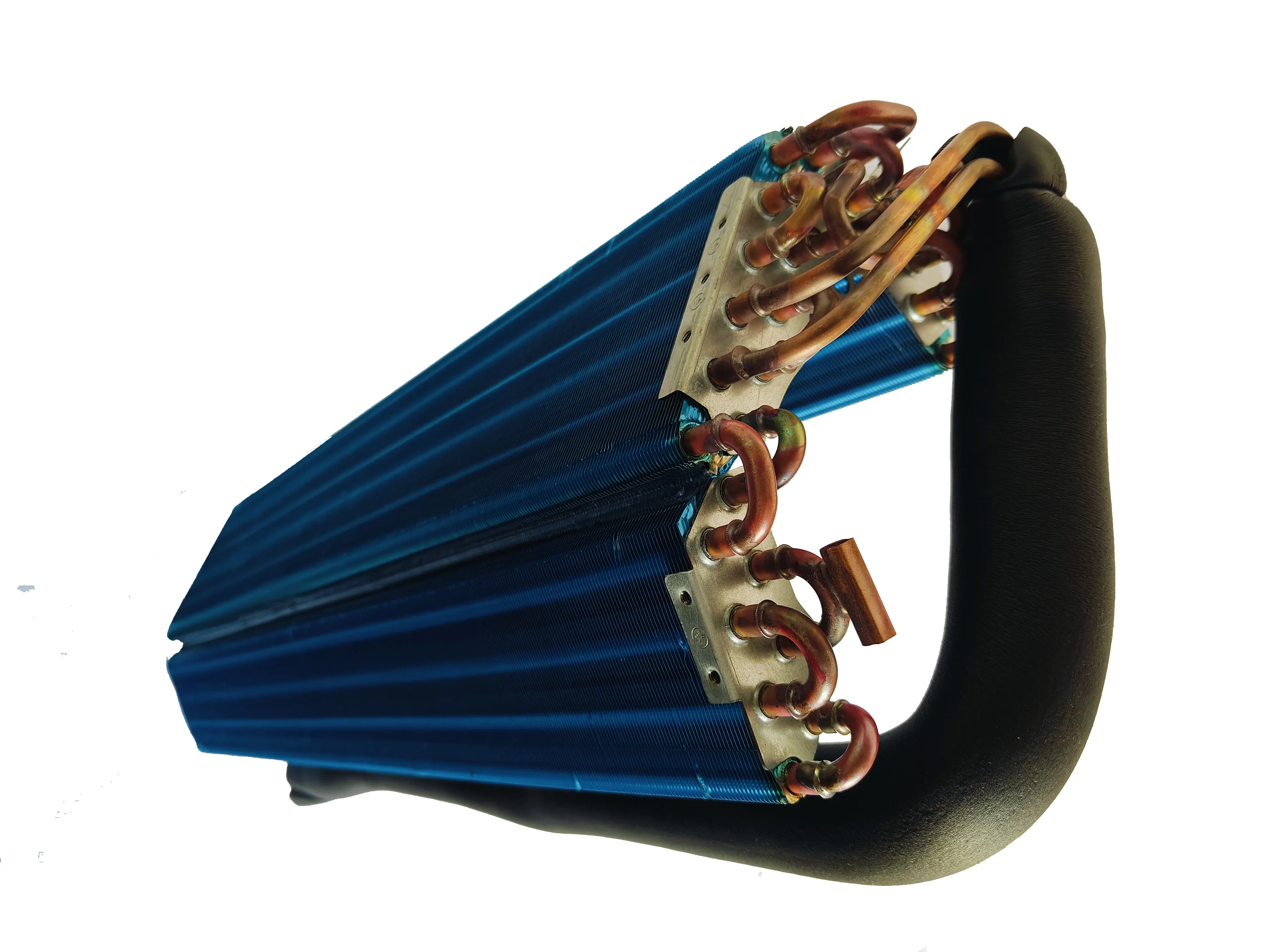
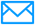
How to design the copper tubes in a heat exchanger: should they be smooth or finned?

When designing a heat exchanger, the choice between smooth or finned copper tubes should be based on a comprehensive consideration of the following factors:
**Heat Transfer Performance**
- **Smooth Tubes**: These have a smooth surface, resulting in relatively simple contact between the refrigerant and the tube wall during flow, and a lower convective heat transfer coefficient. They are suitable for applications with modest heat transfer requirements and straightforward operating conditions.
- **Finned Tubes**: The internal fin structure increases the contact area between the refrigerant and the tube wall, enhancing turbulence and improving heat transfer efficiency. They are ideal for systems with high heat transfer demands, such as refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
**Flow Resistance**
- **Smooth Tubes**: The smooth interior surface minimizes flow resistance, making them suitable for systems with high flow rates and low pressure loss requirements, such as cooling water systems in large chillers.
- **Finned Tubes**: The fin structure increases flow resistance, requiring higher system pressure to maintain refrigerant circulation. However, in systems where some pressure loss is acceptable and heat transfer performance is prioritized, their advantages can outweigh the increased resistance.
**Manufacturing Process and Cost**
- **Smooth Tubes**: These are simpler to manufacture, with higher production efficiency and lower costs, making them suitable for large-scale production and cost-sensitive applications.
- **Finned Tubes**: Specialized equipment and processes are required for manufacturing, resulting in higher costs. However, in high-end products where performance is critical, the increased cost can be justified by the superior performance.
**Fouling and Maintenance**

- **Smooth Tubes**: The smooth surface is less prone to fouling, making cleaning and maintenance easier. Simple rinsing can remove deposits, making them suitable for environments with poor water quality or high fouling potential.
- **Finned Tubes**: The fin structure can accumulate deposits, making cleaning more challenging. However, in systems with stringent hygiene requirements that allow for regular professional cleaning, they can still be used effectively.
**Space and Installation Requirements**
- **Smooth Tubes**: Their smaller outer diameter reduces space requirements, making them advantageous in compact installations. They also offer greater flexibility in layout and installation.
- **Finned Tubes**: The fin structure increases the outer diameter, requiring more space. However, in applications where space is available, their superior heat transfer performance can reduce the overall size and weight of the heat exchanger.