China vs. West: Divergent Technology Paths in Heat Exchanger Design

Heat exchanger design highlights a stark contrast between China and the West. While Western countries focus on advanced materials and energy efficiency, China prioritizes cost-effectiveness and scalability. This divergence stems from their unique industrial needs. For instance:
- Heavy industries in China contribute 31% of its carbon emissions, surpassing global averages.
- Western economies emphasize decarbonization in vehicles, buildings, and power generation.
These priorities drive China's aggressive innovation in heavy industry applications, such as wire tube condensers and Copper Fin Heat Exchanger systems.
Key Takeaways
- China focuses on making heat exchangers cheap and affordable. This helps industries grow fast and expand easily.
- Western companies use better materials and save more energy. Their heat exchangers last longer and work very well. This helps the environment and follows strict rules.
- Knowing how China and the West differ helps industries pick the best heat exchanger for their needs.
Overview of Heat Exchanger Design

What Are Heat Exchangers?
Heat exchangers are devices that transfer heat between two or more fluids without mixing them. These fluids can be gases, liquids, or a combination of both. The primary goal is to either heat or cool a fluid efficiently, depending on the application. Common designs include shell-and-tube, plate, and finned tube heat exchangers. Each type serves specific industrial needs. For instance:
- Shell-and-Tube: Ideal for oil refining and chemical processing due to its ability to handle high pressures and temperatures.
- Plate: Compact and efficient, widely used in HVAC systems and food processing.
- Finned Tube: Features extended surfaces for enhanced heat transfer, making it suitable for air-cooled applications.
Effective fluid flow management plays a critical role in optimizing heat transfer. It ensures uniform distribution and prevents operational inefficiencies, such as hotspots or uneven heating.
Importance in Industrial Applications
Heat exchangers are indispensable in industries where energy efficiency and thermal management are critical. They significantly reduce energy input requirements, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions. For example, industries account for 54% of global electricity consumption, and efficient heat exchangers can save up to $60 billion annually in energy costs.
A case study highlights the advantages of plate heat exchangers over conventional shell-and-tube designs. The plate heat exchangers achieved a heat transfer coefficient two to three times higher, reducing the number of units needed from ten to four. This not only cut retrofit costs but also improved overall system efficiency.
| Efficiency Range | Description |
|---|---|
| 80–95% | Typical efficiency based on actual heat transfer compared to theoretical maximum. |
The growing demand for renewable energy infrastructure further underscores the importance of heat exchangers. As renewable capacity expands, industries increasingly rely on these devices to optimize energy use and meet sustainability goals.
Western Approach
Focus on Advanced Materials
In the Western heat exchanger industry, advanced materials play a pivotal role in achieving superior performance. I’ve observed that manufacturers prioritize materials like stainless steel, copper, and acrylic for their unique properties. Stainless steel, for instance, offers exceptional strength and resistance to high pressures, making it ideal for demanding applications. Copper, on the other hand, stands out for its high thermal conductivity and anti-microbial properties, which enhance heat transfer efficiency.
To illustrate, consider the following table showcasing material choices and their optimization strategies:
| Design Aspect | Material Used | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Shell Material | Acrylic | Provides visibility for monitoring and assessing performance during experiments. |
| Tube Material | Stainless Steel | Chosen for its strength and ability to withstand high pressures in various applications. |
| Baffle Configuration | 2 Baffles | Enhances fluid flow and heat transfer efficiency, validated through experimental results. |
These materials not only improve performance but also ensure durability and reliability in diverse industrial settings. By leveraging such innovations, Western manufacturers maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
Emphasis on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy efficiency and sustainability are at the heart of Western heat exchanger design. I’ve noticed that regulatory bodies in the West enforce strict energy efficiency standards, pushing manufacturers to innovate. Advanced heat exchangers can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, according to studies by the European Heat Pump Association. This aligns with the European Union’s goal of generating 42.5% of its energy from renewable sources by 2030.
Here are some key drivers behind this focus:
- The heat exchanger market is growing due to the demand for effective temperature control in HVAC and refrigeration sectors.
- Energy-efficient designs help industries save operational costs while reducing environmental impact.
- Industrial processes consume nearly 25% of the EU’s total energy, highlighting the need for energy-saving technologies.
Western manufacturers are also exploring renewable energy applications. For example, heat exchangers are now integral to solar thermal systems and geothermal energy projects. These innovations not only support sustainability goals but also position Western companies as leaders in green technology.
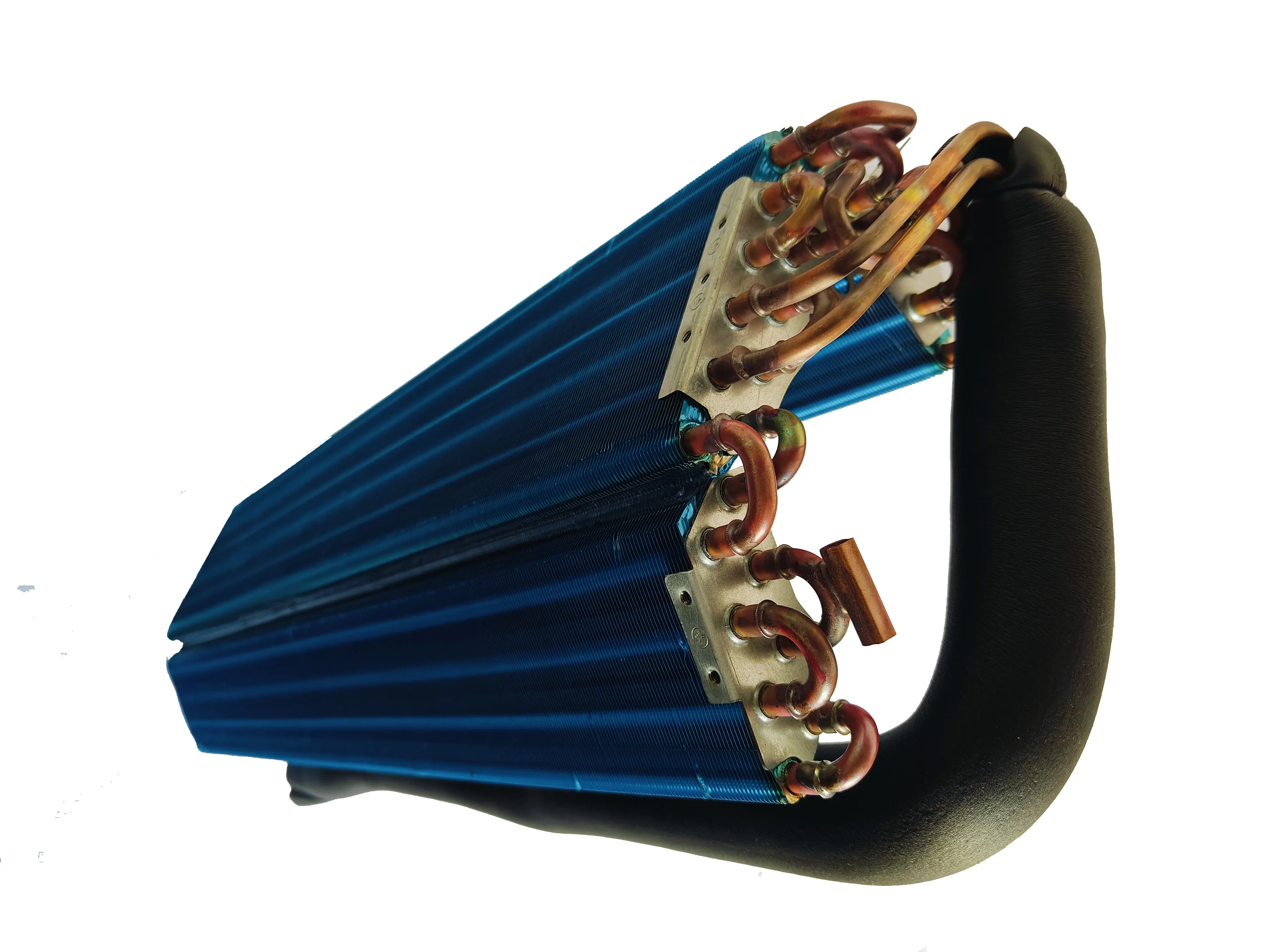
Innovations in Copper Fin Heat Exchanger Design
Western companies have made significant strides in Copper Fin Heat Exchanger design. I’ve seen how these innovations focus on maximizing heat transfer efficiency while minimizing material usage. Copper’s high thermal conductivity makes it an ideal choice for finned designs, which are widely used in HVAC systems, refrigeration, and industrial cooling.
Recent advancements include:
- Enhanced Fin Geometry: Engineers are experimenting with micro-fins and wavy patterns to increase surface area and improve heat transfer rates.
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Protective layers extend the lifespan of Copper Fin Heat Exchangers, especially in harsh environments.
- Compact Designs: Manufacturers are developing smaller, more efficient units to meet space constraints in modern facilities.
These innovations demonstrate the Western commitment to combining performance with sustainability. By optimizing Copper Fin Heat Exchanger designs, companies can deliver solutions that meet both industrial and environmental demands.
Chinese Approach
Prioritization of Cost-Effectiveness
China's heat exchanger industry thrives on its ability to deliver cost-effective solutions. I’ve observed that manufacturers in China prioritize affordability without compromising functionality. This approach aligns with the country's industrial focus on heavy manufacturing and infrastructure development, where cost efficiency is paramount. By utilizing locally sourced materials and streamlined production processes, Chinese companies can significantly reduce manufacturing costs.
For instance, many manufacturers opt for aluminum over copper in certain applications due to its lower cost, despite copper's superior thermal conductivity. This trade-off allows them to produce heat exchangers that meet performance requirements while remaining budget-friendly. Additionally, simplified designs, such as wire tube condensers, further contribute to cost savings. These designs are particularly effective in applications like refrigerators and freezers, where affordability is a key consideration.
Mass Production and Rapid Scalability
China's ability to scale production rapidly sets it apart from other regions. I’ve seen how manufacturers leverage advanced automation and efficient supply chains to achieve unparalleled scalability. This capability enables them to meet the growing global demand for heat exchangers, especially in emerging markets.
Mass production techniques allow Chinese companies to produce large volumes of heat exchangers at competitive prices. For example, the production of Copper Fin Heat Exchangers benefits from automated assembly lines that minimize labor costs and maximize output. This efficiency not only supports domestic needs but also strengthens China's position as a leading exporter of heat exchangers.
Moreover, China's focus on scalability extends to its ability to adapt production lines quickly. When market demands shift, manufacturers can reconfigure their operations to produce new designs or accommodate different materials. This flexibility ensures that Chinese companies remain competitive in a dynamic global market.
Role of Companies Like Senjun in Domestic Innovation
Companies like Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd. play a pivotal role in driving innovation within China's heat exchanger industry. Senjun specializes in the research, development, and production of wire tube condensers and Copper Fin Heat Exchangers. Their products serve a wide range of applications, including refrigerators, freezers, and medical ultra-low temperature refrigerators.
Senjun's success stems from its customer-centric approach. The company focuses on understanding customer needs, which drives innovation in product development. By predicting market changes, Senjun adapts its offerings to stay ahead of industry trends. For example, their use of advanced technology and creative thinking enhances both product performance and service quality.
Additionally, Senjun's commitment to innovation extends to its manufacturing processes. The company employs cutting-edge techniques to improve the efficiency and reliability of its heat exchangers. This dedication not only strengthens its domestic market position but also contributes to the global competitiveness of China's heat exchanger industry.
Key Drivers of Divergence
Economic Factors
Economic priorities significantly shape the divergent paths in heat exchanger design between China and the West. I’ve noticed that Western manufacturers often operate in high-cost environments, where labor, materials, and energy expenses drive innovation toward efficiency and durability. These companies invest heavily in advanced materials and cutting-edge technologies to justify higher price points.
In contrast, China’s focus on cost-effectiveness stems from its role as a global manufacturing hub. Chinese companies, like Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd., excel at producing affordable solutions by leveraging economies of scale and local resources. This approach allows them to dominate price-sensitive markets, particularly in developing regions.
Insight: Western firms prioritize long-term savings through efficiency, while Chinese manufacturers focus on upfront affordability to meet immediate market demands.
Cultural Influences
Cultural values also play a pivotal role in shaping design philosophies. Western cultures often emphasize individual innovation and environmental responsibility. This mindset drives companies to develop sustainable, high-performance products that align with global decarbonization goals.
In China, the collective focus on rapid industrial growth and practical solutions fosters a culture of adaptability. I’ve observed how this adaptability enables Chinese manufacturers to respond quickly to market changes, ensuring they remain competitive. This cultural emphasis on pragmatism often results in streamlined designs that prioritize functionality over complexity.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Government policies and regulations further amplify these differences. Western nations enforce stringent environmental standards, pushing manufacturers to adopt energy-efficient technologies. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal incentivizes the development of sustainable heat exchangers.
China’s regulatory framework, while evolving, prioritizes industrial growth and infrastructure development. Policies often support mass production and export-oriented strategies. Companies like Senjun benefit from these policies, which encourage innovation in cost-effective manufacturing techniques.
Takeaway: Regulatory environments reflect regional priorities, shaping the trajectory of heat exchanger design in distinct ways.
Comparative Analysis

Strengths of the Western Approach
The Western approach to heat exchanger design excels in innovation and sustainability. I’ve observed that Western manufacturers prioritize advanced materials like stainless steel and copper, which enhance durability and thermal efficiency. This focus ensures long-term reliability in demanding applications.
Energy efficiency also stands out as a key strength. Western companies invest heavily in technologies that reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. This aligns with strict environmental regulations and the growing demand for sustainable solutions. For example, compact heat exchangers, such as printed circuit heat exchangers (PCHEs), are widely used in advanced reactors and power cycles due to their high thermal efficiency.
Additionally, Western firms lead in renewable energy integration. Heat exchangers designed for solar thermal and geothermal systems demonstrate their commitment to green technology. These innovations position Western companies as global leaders in sustainable industrial solutions.
Strengths of the Chinese Approach
China’s heat exchanger industry thrives on cost-effectiveness and scalability. I’ve noticed that Chinese manufacturers, like Ningbo Senjun New Materials Co., Ltd., excel at producing affordable solutions without compromising functionality. This approach makes their products highly competitive in price-sensitive markets.
The rapid adoption of microchannel heat exchangers highlights China’s strengths.
- The Asia-Pacific region, led by China, dominates this market due to urbanization and increased construction activities.
- Government support and research investments enhance the quality and affordability of these systems.
- The focus on energy conservation and pollution reduction aligns with regulatory efforts to reduce emissions.
Mass production capabilities further strengthen China’s position. Automated assembly lines and efficient supply chains enable manufacturers to meet global demand quickly and cost-effectively.
Weaknesses and Challenges in Both Approaches
Both approaches face unique challenges. Western designs often struggle with high costs, limiting their accessibility in developing markets. Advanced materials and technologies, while effective, increase production expenses.
Chinese designs, on the other hand, face structural and performance challenges in high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Studies on PCHEs reveal issues like mechanical integrity under extreme conditions. For example:
| Study Title | Key Findings | Challenges Identified |
|---|---|---|
| Compact Heat Exchanger Design and Testing for Advanced Reactors and Advanced Power Cycles | Focus on PCHEs in GFRs and their role in heat transfer | Structural strength under high pressure, thermal efficiency issues |
| Development of an Integrated Design Evaluation ‘HITEP’ Platform | Software for evaluating high-temperature pressure components | Reliability in high-temperature operations, creep range challenges |
| Preliminary structural assessment of a printed circuit heat exchanger with S-Shaped fins | Mechanical integrity assessment of PCHEs | Structural challenges due to high operating pressures of s-CO2 |
These challenges highlight the need for continuous innovation and collaboration to overcome technical and economic barriers in both regions.
China and the West take distinct paths in heat exchanger design. The West emphasizes advanced materials and energy efficiency, while China focuses on cost-effectiveness and scalability. These approaches reflect their industrial priorities—decarbonization in the West and rapid industrial growth in China.
Note: Both regions excel in addressing their unique challenges, showcasing innovation tailored to their needs.
Future trends suggest a global convergence in heat exchanger technologies. The hybrid heat exchanger market is growing due to energy efficiency regulations and sustainable practices. Emerging economies, particularly in Asia-Pacific, drive this demand. Technological advancements, such as smart technologies and advanced materials, further reshape the market.
| Key Trends in Heat Exchanger Design | Highlights |
|---|---|
| Market Growth | Driven by energy efficiency demands and regulatory pressures. |
| Regional Expansion | Significant growth in North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific. |
| Material and Design Innovations | Compact, efficient designs with high-performance alloys. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Supports sustainability and waste heat recovery systems. |
These trends indicate opportunities for collaboration, blending Western innovation with China's scalability to meet global industrial needs.
FAQ
What makes heat exchangers critical in industrial applications?
Heat exchangers optimize energy use by transferring heat efficiently. This reduces operational costs and supports sustainability goals in industries like HVAC, power generation, and manufacturing.
How does Senjun contribute to China's heat exchanger industry?
Senjun drives innovation by producing cost-effective wire tube condensers and Copper Fin Heat Exchangers. Their solutions serve diverse applications, from medical refrigeration to dehumidifiers.
Why do Western manufacturers prioritize advanced materials?
Western manufacturers focus on advanced materials like stainless steel and copper to enhance durability, thermal efficiency, and compliance with strict environmental regulations.
Tip: Understanding regional priorities helps in selecting the right heat exchanger for specific industrial needs.